Holland’s Theory of Career Choice and You
How Holland’s Theory helps you choose the right career path
Holland’s Theory helps you choose a career or education program that fits your personality and interests. Research shows that when you do that, you take a vital step toward career well-being and success. Success means you feel good and perform better in your job and in school. You want to answer, "Yes!" to the question, "Do you like what you do each day?"
Dr. John Holland’s Theory, also known as Holland’s theory of vocational choice, is the best known and most widely researched theory about where we thrive in our work. It’s widely used by career development professionals, measured with a career interest inventory. Sometimes you hear it referred to as Holland Codes, but there is so much more to it than labeling someone as a three-letter code.
Understanding the theory helps you identify careers and education programs that fit who you are and put you on the right path to career well-being.
Summary of Holland's theory:
In our culture, most people are one of six personality types:
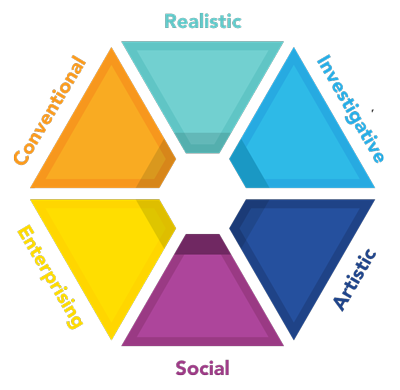
Realistic, Investigative, Artistic, Social, Enterprising, and Conventional. Some refer to these as Holland Codes or RIASEC.
People of the same personality type working together create a work environment that fits their type. For example, when Artistic persons are together on a job, they create a work environment that rewards creative thinking and behavior -- an Artistic environment.
There are six basic types of work environments:
Realistic, Investigative, Artistic, Social, Enterprising, Conventional. "Work" includes doing things to achieve a purpose, like paid and unpaid jobs, volunteering, sports, or hobbies.
People search for environments where they can use their skills and abilities and express their values and attitudes.
For example, Investigative types search for Investigative environments; Artistic types look for Artistic environments, and so forth.
People who choose to work in an environment similar to their personality type are more likely to be successful and satisfied.
For example, Artistic people are more likely to be successful and satisfied if they choose a job that has an Artistic environment, like choosing to be a dance teacher in a dancing school -- an environment "dominated" by Artistic type people where creative abilities and expression are highly valued.
6. How you act and feel at work depends to a large extent on your workplace (or education) environment.
If you are working with people who have a personality type like yours, you will be able to do many of the things they can do, and you will feel most comfortable with them.
Next step: Match your personality to compatible environments
Choosing work or an education program that matches, or is similar to your personality, will most likely lead to success and satisfaction. This good match is called "congruent" (meaning compatible, in agreement or harmony).
So for example, imagine you score highest for the Realistic type on the Career Key Discovery assessment. On the table below, you see that your most compatible work environment is Realistic, a congruent match. It's best if you choose a Realistic job, or you might also choose Investigative or Conventional jobs.
Compatible Work Environments
Your Personality Type
Realistic
Investigative
Artistic
Social
Enterprising
Conventional
Most Compatible
Realistic
Investigative
Artistic
Social
Enterprising
Conventional
Other Compatible
Most people, in reality, are a combination of types–like Realistic-Investigative, or Artistic-Social. Therefore, you will probably want to consider occupations in more than one category.
In summary, you are most likely to choose a satisfying work if you choose to do something that fits your personality type.
If your two strongest personality types are "inconsistent"–Realistic and Social, Investigative and Enterprising, or Artistic and Conventional–be sure to read the next section, below, and this article on inconsistent combinations.
Holland's Hexagon
John Holland created a hexagonal model that shows the relationship between the personality types and environments.
Notice that the personality types closest to each other are more alike than those farther away. You can see this most clearly when you compare the personalities opposite each other, on the hexagon. For example, read the description of the types for Realistic and Social. You will see that they are virtually the opposite of each other. On the other hand, Social and Artistic are not that far apart.
The same holds true for the work environments. Read their descriptions and you will see.
See how the hexagon reflects introversion and extroversion; personality-environment match applies to those dimensions also.
Inconsistent Personality Patterns
If your two strongest personality types are Realistic and Social, Investigative and Enterprising, or Artistic and Conventional, read about inconsistent personality patterns and how they can work to your advantage.
Two requirements for using Holland's theory
To benefit from Holland's theory, you must use a:
Valid (accurate) measure of Holland's personality types, supported by published research, and
List of careers and education programs that are accurately assigned to the correct personality types.
The assessments in PathAdvisor and Career Key Discovery meet these two requirements. See below how it helps you apply Holland’s Theory to best-fit work and education environments.